കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ഓക്സൈഡ്
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cobalt(II) oxide
| |
| Other names
Cobaltous oxide
Cobalt monoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.777 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 3288 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| InChI | |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
| CoO | |
| Molar mass | 74.9326 g/mol |
| Appearance | black powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| സാന്ദ്രത | 6.44 g/cm3 [1] |
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |
| insoluble in water[2] | |
| +4900.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic (T) Harmful (Xn) |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
202 mg/kg |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 1551 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Cobalt(II) sulfide Cobalt(II) hydroxide |
| Other cations | Iron(II) oxide Nickel(II) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
കോബാൾട്ട് അടങ്ങിയ ഒരു അജൈവ സംയുക്തമാണ് കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ഓക്സൈഡ് അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കോബാൾട്ട് മോണോക്സൈഡ്. [3] നീല നിറമുള്ള ഗ്ലേസുകളും ഇനാമലുകളും സൃഷ്ടിക്കുന്നതിനും കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ലവണങ്ങൾ ഉൽപാദിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള രാസ വ്യവസായത്തിലും സെറാമിക് വ്യവസായത്തിൽ ഒരു ഒരു സങ്കലനമായും ഇത് വ്യാപകമായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
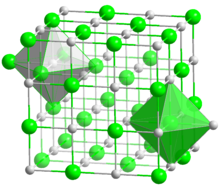
ഘടനയും സവിശേഷതകളും
[തിരുത്തുക]CoO പരലുകൾ 4.2615 of എന്ന ലാറ്റിസ് സ്ഥിരാങ്കം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് പെരിക്ലേസ് ( റോക്ക് സാൾട്ട് ) ഘടന സ്വീകരിക്കുന്നു. [4]
ഇത് 16 °C. ന് താഴെ ആന്റിഫെറോ മാഗ്നറ്റിക് ആണ് [5]
തയ്യാറാക്കൽ
[തിരുത്തുക]കോബാൾട്ട് (II, III) ഓക്സൈഡ് 950 °C ൽ കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ഓക്സൈഡായി വിഘടിക്കുന്നു
- 2 Co3O4 → 6 CoO + O2
കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ക്ലോറൈഡിന്റെ ഒരു ലായനി വൈദ്യുതവിശ്ലേഷണം ചെയ്ത് ലബോറട്ടറിയിൽ കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ഓക്സൈഡ് തയ്യാറാക്കാം. [6]
CoCl2 + H2O → CoO + H2 + Cl2
ഹൈഡ്രോക്സൈഡ് നിർജ്ജലീകരണം നടത്തിയും ഇത് തയ്യാറാക്കാം:
- CoX + 2 KOH → Co(OH)2 + K2X
- Co(OH)2 → CoO + H2O
പ്രതികരണങ്ങൾ
[തിരുത്തുക]കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ഓക്സൈഡ് ധാതു ആസിഡുകളുമായി പ്രതിപ്രവർത്തിച്ച് അനുബന്ധ കോബാൾട്ട് ലവണങ്ങൾ ഉണ്ടാക്കുന്നു:
- CoO + 2 HX → CoX2 + H2O
ഉപയോഗങ്ങൾ
[തിരുത്തുക]കോബാൾട്ട് (II) ഓക്സൈഡ് നൂറ്റാണ്ടുകളായി ചൂളയിൽ നിർമ്മിക്കുന്ന മൺപാത്രങ്ങളിൽ കളറിംഗ് ഏജന്റായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. അഡിറ്റീവായ കോബാൾട്ട് ബ്ലൂ നീലയുടെ ആഴത്തിലുള്ള നിഴൽ നൽകുന്നു.
ഇതും കാണുക
[തിരുത്തുക]- കോബാൾട്ട് ഓക്സൈഡ് നാനോകണങ്ങൾ
- കോബാൾട്ട്
- കോബാൾട്ട് (II, III) ഓക്സൈഡ്
അവലംബം
[തിരുത്തുക]- ↑ Patnaik, Pradyot (2003). Handbook of Inorganic Chemical Compounds. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-049439-8. Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- ↑ Advanced Search – Alfa Aesar – A Johnson Matthey Company Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine. Alfa.com. Retrieved on 2011-11-19.
- ↑ "Safety (MSDS) data for cobalt oxide". The Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory, Oxford University. Archived from the original on 2010-10-28. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- ↑ Kannan, R.; Seehra, Mohindar S. (1987). "Percolation effects and magnetic properties of the randomly diluted fcc system CopMg1-pO". Physical Review B. 35 (13): 6847–6853. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.35.6847.
- ↑ Silinsky, P. S.; Seehra, Mohindar S. (1981). "Principal magnetic susceptibilities and uniaxial stress experiments in CoO". Physical Review B. 24: 419–423. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.24.419.
- ↑ Kern, S. (1876). "Inorganic chemistry". J. Chem. Soc. 29: 880. doi:10.1039/JS8762900876.
- Pages using the JsonConfig extension
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Pages using Chembox with unknown parameters
- ഓക്സൈഡുകൾ

