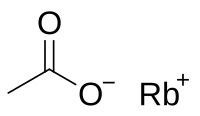
റുബിഡിയം അസറ്റേറ്റ്
ദൃശ്യരൂപം
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Rubidium acetate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.415 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| InChI | |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
| Molar mass | 144.51 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |
| 85 g/100 ml (45 °C)[1] | |
| log P | -0.561 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| H305, H315 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | rubidium formate |
| Other cations | Hydrogen acetate Lithium acetate Sodium acetate Potassium acetate Caesium acetate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
റുബിഡിയം ലോഹം, റുബിഡിയം കാർബണേറ്റ് അല്ലെങ്കിൽ റുബിഡിയം ഹൈഡ്രോക്സൈഡ് എന്നിവ അസറ്റിക് ആസിഡിൽ ലയിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ഫലമായുണ്ടാകുന്ന ഒരു റുബിഡിയം സംയുക്തമാണ് റുബിഡിയം അസറ്റേറ്റ്. മറ്റ് അസറ്റേറ്റുകളെപ്പോലെ ഇത് വെള്ളത്തിൽ ലയിക്കുന്നു. [2][1][3] [4]
ഉപയോഗം
[തിരുത്തുക]റുബിഡിയം അസറ്റേറ്റ് സിലനോൾ ടെർമിനേറ്റഡ് സിലോക്സെയ്ൻ ഒലിഗോമറുകളുടെ പോളിമറൈസേഷനായി ഒരു രാസത്വരകമായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. [5]
അവലംബം
[തിരുത്തുക]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "CXRB010_ RUBIDIUM ACETATE, monohydrate" (PDF). Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- ↑ "Rubidium acetate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ "RUBIDIUM ACETATE | 563-67-7". www.chemicalbook.com.
- ↑ "Safety data sheet" (PDF). s3.amazonaws.com. 2015. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- ↑ "Rubidium acetate". gelest.com. Archived from the original on 2021-11-22. Retrieved 2021-11-22.

