ബർത്തോലിൻസ് സിസ്റ്റ്
| Bartholin's cyst | |
|---|---|
| മറ്റ് പേരുകൾ | Bartholin duct cyst, Bartholin gland cyst, cyst of Bartholin gland[1] |
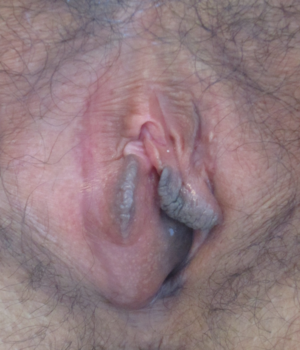 | |
| Bartholin's cyst of the right side | |
| സ്പെഷ്യാലിറ്റി | Gynecology |
| ലക്ഷണങ്ങൾ | Swelling of one side of the vagina, pain, sometimes no symptoms[1] |
| സങ്കീർണത | Abscess[2] |
| സാധാരണ തുടക്കം | Childbearing age[2] |
| കാരണങ്ങൾ | Unknown[3] |
| ഡയഗ്നോസ്റ്റിക് രീതി | Based on symptoms and examination[3] |
| ഡിഫറൻഷ്യൽ ഡയഗ്നോസിസ് | Sebaceous cyst, hernia, hidradenitis suppurativa, folliculitis, vulvar cancer[4][5] |
| Treatment | Placement of a Word catheter, incision and drainage, marsupialization, sitz baths[4][3] |
| ആവൃത്തി | 2% of women[2] |
ലാബിയയ്ക്കുള്ളിൽ ബാർട്ടോലിൻ ഗ്രന്ഥി തടസ്സപ്പെടുമ്പോൾ ബർത്തോലിൻസ് സിസ്റ്റ് സംഭവിക്കുന്നു. [3] ചെറിയ സിസ്റ്റുകൾ ചുരുങ്ങിയതോ ലക്ഷണങ്ങളോ ഉണ്ടാക്കുന്നില്ല. [1]വലിയ സിസ്റ്റുകൾ യോനിയുടെ ഒരു വശത്ത് വീക്കം ഉണ്ടാകാം, അതുപോലെ ലൈംഗികതയിലോ നടക്കുകമ്പോഴോ വേദനയുണ്ടാകാം.[3] സിസ്റ്റ് രോഗം ബാധിച്ചാൽ, കുരു ഉണ്ടാകാം. അത് സാധാരണയായി ചുവപ്പും വേദനാജനകവുമാണ്. [2] ലക്ഷണങ്ങളൊന്നുമില്ലെങ്കിൽ, ചികിത്സ ആവശ്യമില്ല. [2][3] ബാർട്ടോലിൻ സിസ്റ്റുകൾ ജീവിതത്തിലെ ചില ഘട്ടങ്ങളിൽ ഏകദേശം 2% സ്ത്രീകളെ ബാധിക്കുന്നു. [2] പ്രസവകരമായ വർഷങ്ങളിൽ അവ സാധാരണയായി സംഭവിക്കുന്നു.[2]
പാത്തോഫിസിയോളജി
[തിരുത്തുക]ഗ്രന്ഥി മുറിഞ്ഞ് നാളം തടയുമ്പോൾ ബർത്തോലിൻസ് ഗ്രന്ഥി സിസ്റ്റ് വളരുന്നു. [6] തടസ്സം അല്ലെങ്കിൽ മ്യൂക്കസ് പ്ലഗ് മൂലമുണ്ടാകാം. [6]ബർത്തോലിൻസ് ഗ്രന്ഥിയുടെ സ്രവങ്ങൾ നിലനിർത്തി, ഒരു സിസ്റ്റ് രൂപപ്പെടുന്നു.[2]
എപ്പിഡെമിയോളജി
[തിരുത്തുക]രണ്ട് ശതമാനം സ്ത്രീകൾക്ക് അവരുടെ ജീവിതത്തിലെ ചില ഘട്ടത്തിൽ ബർത്തോലിൻസ് ഗ്രന്ഥി സിസ്റ്റ് ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കും. [2] 1000 വ്യക്തികൾക്ക് 0.55 എന്ന നിരക്കിൽ അവ സംഭവിക്കുന്നത്, 35-50 വയസ്സുള്ള സ്ത്രീകളിൽ 1000 വ്യക്തികൾക്ക് 1.21 എന്ന നിരക്കിൽ സംഭവിക്കുന്നു. [7]ആർത്തവവിരാമം വരെ ബർത്തോലിൻസ് ഗ്രന്ഥി സിസ്റ്റുകൾ വർദ്ധിക്കുന്നു, അതിനുശേഷം കുറയുന്നു. [7] ഹിസ്പാനിക് സ്ത്രീകൾക്ക് വെളുത്ത സ്ത്രീകളെയും കറുത്ത സ്ത്രീകളെയും അപേക്ഷിച്ച് പലപ്പോഴും ബാധിച്ചേക്കാം.[2] പ്രസവങ്ങളുടെ എണ്ണം അനുസരിച്ച് ബർത്തോലിൻസ് ഗ്രന്ഥി സിസ്റ്റ് വികസിപ്പിക്കാനുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്.
അവലംബം
[തിരുത്തുക]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, ed. (2020). "10. Tumours of the vulva: Bartholin gland cyst". Female genital tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours. Vol. 4 (5th ed.). Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer. p. 440. ISBN 978-92-832-4504-9.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 Omole, Folashade; Simmons, Barbara J.; Hacker Yolanda (2003). "Management of Bartholin's duct cyst and gland abscess". American Family Physician. 68 (1): 135–40. PMID 12887119.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "Bartholin Gland Cysts". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lee, MY; Dalpiaz, A; Schwamb, R; Miao, Y; Waltzer, W; Khan, A (May 2015). "Clinical Pathology of Bartholin's Glands: A Review of the Literature". Current Urology. 8 (1): 22–5. doi:10.1159/000365683. PMC 4483306. PMID 26195958.
- ↑ Ferri, Fred (2017). Ferri's clinical advisor 2018 : 5 books in 1. Elsevier Canada. p. 175. ISBN 978-0323280495.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Eilber, Karyn Schlunt; Raz, Shlomo (September 2003). "Benign Cystic Lesions of the Vagina: A Literature Review". The Journal of Urology. 170 (3): 717–722. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000062543.99821.a2. PMID 12913681.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Yuk, Jin-Sung; Kim, Yong-Jin; Hur, Jun-Young; Shin, Jung-Ho (2013). "Incidence of Bartholin duct cysts and abscesses in the Republic of Korea". International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. 122 (1): 62–4. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2013.02.014. PMID 23618035. S2CID 23981470.
External links
[തിരുത്തുക]| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
